Bacterial flagella are thread-like appendages, protruding from the cell wall, they confer motility to the bacteria (organs of locomotion). They measure 5-20 μm in length and 0.01- 0.02 μm in thickness.
Arrangement of bacterial flagella
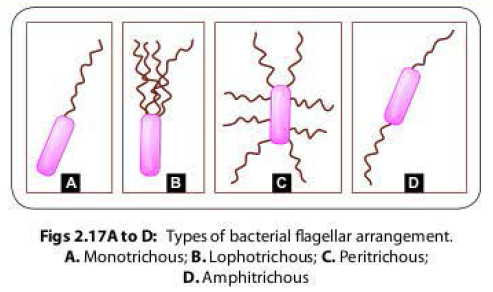
There are various patterns of arrangement of bacterial flagella with respect to the bacterial surface (Fig; 2.17):
- Monotrichous (single polar flagellum), e.g. Vibirio cholerae, Pseuodomonas and Campylobacter
- Lophotrichous (multiple polar flagella), e.g. Spirillum.
- Peritrichous (flagella distributed over the entire cell surface)-e.g. Salmonellsa typhi, Escherichia coli.
- Amphitrichous (single flagellum at both the ends)- e.g. Alcaligenes faecalis
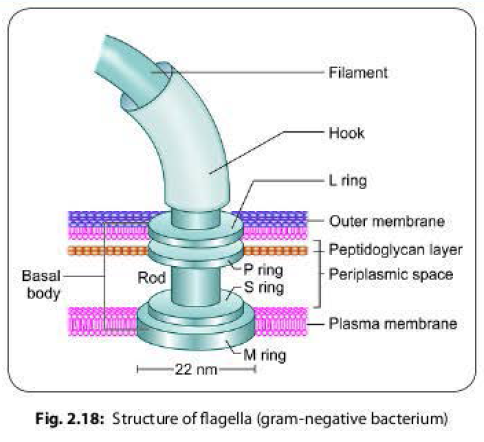
Ultra-structure of bacterial flagella
Electron microscope reveals that the bacterial
flagellum is composed of three parts (Fig. 2.18).
- Filament: It is the longest portion of the flagellum that extends from the cell surface to the tip. It is a hollow, rigid cylinder, made up of a single protein flagellin.
- The basal body: This is the portion of flagellum which is embedded in the cell. It is the most complex part of a flagellum, made up of 2-4 rings connected to a central rod.
- In most gram-negative bacteria, there are four rings named as-
- The outer L and P rings associate with the LPS and peptidoglycan layers, respectively.
- The inner S ring lies in periplasmic space and M ring contacts the plasma membrane.
- Gram-positive bacteria have only two basal body rings, an inner ring connected to the plasma membrane and an outer one probably attached to the peptidoglycan.
- Hook: It is a short, curved flexible segment that links the filament to its basal body.
Detection
of bacterial flagella
Flagella can be demonstrated by:
Direct demonstration of flagella:
- Tannic acid staining (Leifson's method and Ryu's method)
Indirect means by demonstrating the
motility:
- Cragie tube method
- Hanging drop method
- Semisolid medium, e.g. mannitol motility medium
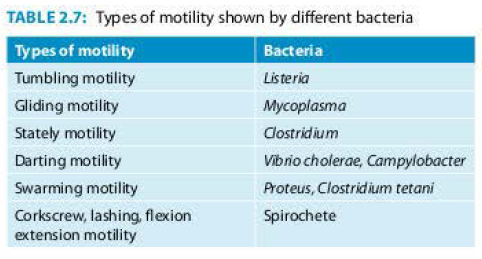
Bacterial Motility
Bacteria can produce characteristic type of motility which helps in their identification (Table 2. 7).

No comments:
Post a Comment