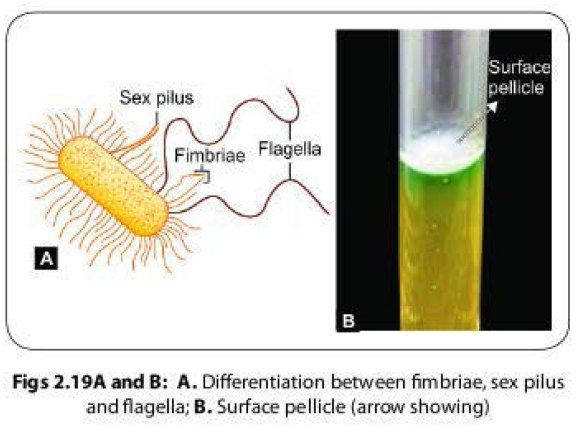
Bacterial fimbriae or pili are short, fine, hair-like appendages that are thinner than flagella and not involved in motility(singular fimbria or pilus).
Pili are
made up of protein called pilin.
Bacterial fimbriae are antigenic; however, the antibodies against fimbrial antigens are not protective.
Fimbriae are very small, measuring 0.5μm long and10 nm in thickness. A bacterium can have as many as 1,000 fimbriae.
Functions of
- Fimbriae are called the organ of adhesion. This property enhances the virulence of bacteria.
- Certain fimbriae called sex pili also help in bacterial gene transfer.
- Fimbriae are not related to motility and can be found both in motile as well as in non-motile organisms.
Types
Different types of fimbriae are as follows (Fig.
2.19A)-
- Common pili: There are six types of common pili depending on their morphology, number per cell, adhesive properties and antigenic nature.
- Sex or F (fertility) pill:
- Sex pili are special type of large fimbriae present 1-10 per cell (e.g. as found in gonococcus).
- Sex pili help in bacterial conjugation.
- They are present in male bacterium; form the conjugation tube in male bacterium and thereby help in transfer of genetic material from male bacteria to the female bacteria via the conjugation tube.
- Col I (colicin) pili.
Detection of
Electron microscopy is the only method for direct demonstration of fimbriae. However, there are some indirect methods to know the presence of fimbriae such as:
Hemagglutination:
- Many fimbriated bacteria (e.g. Escherichia coli, Klebsiella) strongly agglutinate with red blood cells of guinea pigs, fowl, horses and pigs.
- This property of hemagglutination is a simple method for detecting the presence of fimbriae.
- In some bacteria, the hemagglutination may be specifically inhibited by D-mannose.
Surface pellicle:
- Some aerobic fimbriated bacteria form a thin layer at the surface of a broth culture called as pellicle.
- The pellicle consists of many aerobic bacteria that adhere to the surface by their fimbriae (Fig. 2.198).

هلا
ReplyDeleteBio student here. What I remember in my gen microbio class is that bacterial pili is commonly used in horizontal gene transfer
ReplyDeleteYes, that's correct!
DeleteNice Very Interesting
ReplyDelete