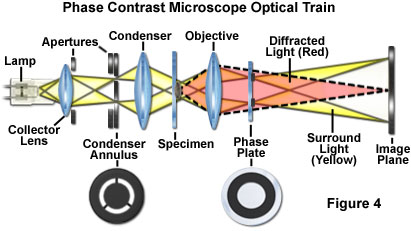
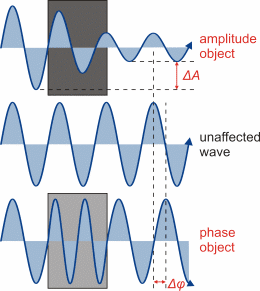
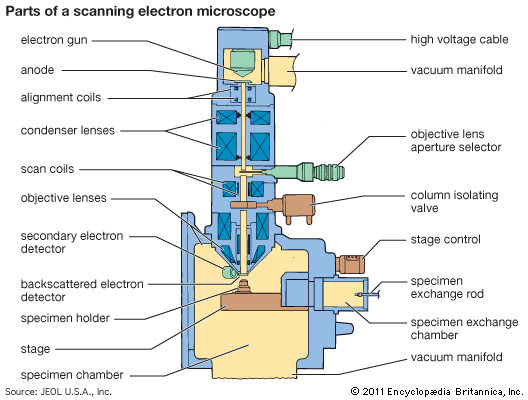
PRINCIPLE:
- Retardation by a fraction of a wavelength, of the rays of light that pass through the object, compared to the rays passing through the surrounding medium, produces the ‘phase’ differences between the two types of rays.
- In the phase contrast microscope, ‘phase’ differences are converted into differences in intensity of light, producing light & dark contrast in the image.
USES OF PHASE CONTRAST MICROSCOPE:
- For detecting bacterial components such as endospores and inclusion bodies which become clearly visible because they have refractive indices markedly different from that of water.
- For examining live unstained microorganisms in a suspending fluid.
- Microbial motility.
- Determine the shape of living cells
PRINCIPLE:
- In electron microscope a beam of electrons is focused by a circular electromagnet (magnetic condenser).
- When an electron beam passes through the object, the electrons get scattered producing an image in the built in fluorescent viewing screen.
- The wavelength of electrons employed is approximately 0.005 nm. Resolving power is about 0.01-0.02 nm.
TYPES:
- There are two types of electron microscopes in general use: the Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM), which has many features in common with the light microscope, and the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM).
- TEM can resolve particles 0.001 nm apart. Viruses, with diameters of 0.01–0.2 nm, can be easily resolved.
- The SEM generally has a lower resolving power than the TEM; however, it is particularly useful for providing three-dimensional images of the surface of microscopic objects.
OTHER TYPES OF MICROSCOPES:
- INTERFERENCE MICROSCOPE: It not only reveals cell organelles but also enables quantitative measurement of chemical constituents of the cells such as lipids, proteins, & nucleic acids.
- POLARISATION MICROSCOPE: It enables the
study of intracellular structures using differences in birefringence.