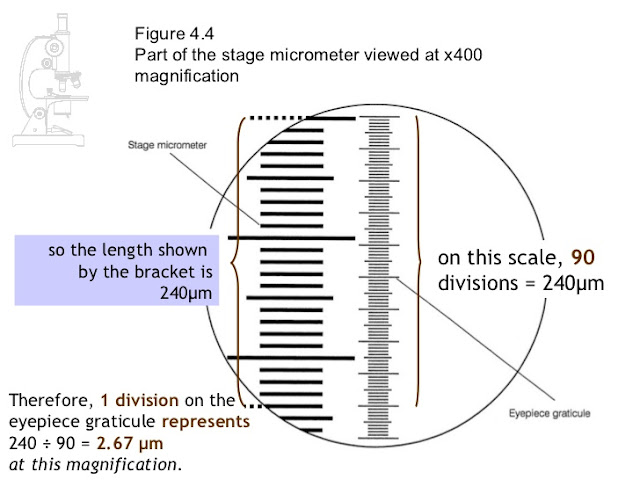
PRINCIPLE OF MICROMETRY:
The measurement of microscopic objects is accomplished
with a micrometer eyepiece, the scale in which is calibrated by comparison with
standard stage micrometer.
The micrometer eyepiece is a special eyepiece, which
bears a graduated scale mounted on its diaphragm and has a movable lens.
The stage micrometer is a microscope slide bearing an engraved scale 1 mm in length and graduated interval of 0.01 mm.
PROCEDURE OF MICROMETRY:
1. Insert the micrometer eyepiece into the eyepiece tube
of the microscope. Focus the eyepiece scale with the movable eyepiece lens.
2. Place the stage micrometer on the microscope stage in
firm contact with its surface. Center the scale in the field.
3. With the objective to be used for micrometer, focus the
scale of stage micrometer and move the stage so that ‘O’ scale of eyepiece
micrometer matches with ‘O’ scale of stage micrometer. (the two scales to be
superimposed on each other from their starting points)
4. Count the number of division on eyepiece scale that
corresponds to a definitive division on stage scale.
5. Remove the stage micrometer & replace it with a
slide bearing the specimen to be studied. The number of divisions of the
eyepiece scale which just cover object are noted. Tube length of the microscope
must not be altered between calibration & measurement.
6. Calculate the measurement of the object.
EXAMPLE:
lf 100 divisions of the eyepiece scale cover 1 division
of the stage micrometer then,
100 eyepiece divisions = 1 stage division
1 stage division = 0.01mm
1 eyepiece division = 0.01 stage division
Hence 1 eyepiece division = 0.01 x 0.01 mm = 0.0011 mm =
1.1 µm.
Now, stained peripheral smear is substituted. See how many
division of eyepiece are covered by RBC.
lf it is 7 divisions then size of RBC = 7 x 1.1 µm = 7.7
µm.
APPROXIMATE
SIZE OF BACTERIA:
0.2-1.5 µm in diameter and 3-5 µm
in length.
PARAMETERS:
1 µm = 1/1000 mm.
1 mµ (or nm) = 1/1000 µm = one millionth of a millimeter.
1Å = 1/10 nm.