DIFFERENT METHODS OF ANTIBIOTIC SUSCEPTIBILITY TESTING
- Muller Hinton agar (MHA) (pH 7.2-7.4) is poured in plates of 9-10 cm, depth of agar is 3-4 cm.
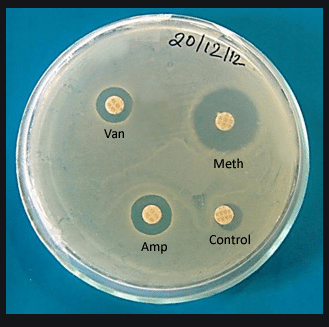
METHOD OF KIRBY-BAUER DISC DIFFUSION
- Five colonies of the test organism are transferred to 5 ml of trypticase soy broth or nutrient broth, incubated at 37°C for 2-4 hours.
- Inoculum standardized by matching the turbidity with 0.5 McFarland standard [0.5 ml of 1.175% barium chloride dehydrate solution added to 99.5 ml N/36 (1%) sulfuric acid].
- With a sterile cotton swab the test culture is spread evenly over the plate successively in 3 directions, to obtain an even inoculum.
- The plate is allowed to dry for 3-5 min. antibiotic discs (diameter 6.35 mm) of correct potency are placed on the surface, 15 mm from the edge of the plate with a distance of 24 mm between discs.
- Not more than 6 discs should be used per plate of 9 cm diameter.
INCUBATION OF KIRBY-BAUER DISC DIFFUSION
- The plate is incubated at 37°C for 18 hours.
INTERPRETATION/ZONES OF INHIBITION OF KIRBY-BAUER DISC DIFFUSION
- The zone of inhibition is measured by a scale to the nearest mm, including disc diameter.
- Zone size is interpreted as Sensitive, Intermediate or Resistant by referring to a table of critical diameters.
CONTROLS FOR OF KIRBY-BAUER DISC DIFFUSION
- Standard control strains should be used.
- When new batch of discs is put into use.
- When new batch of medium is put into use.
- Once in a week in parallel with routine antibiogram.
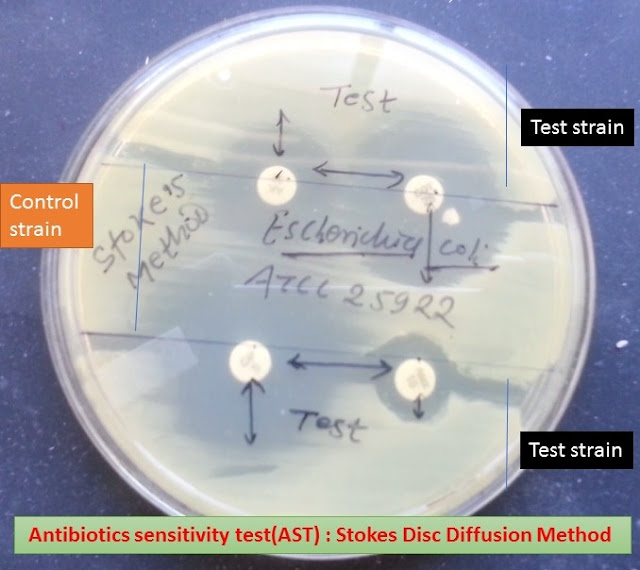
STOKES DISC DIFFUSION METHOD
- Muller Hinton agar (MHA) (pH 7.2-7.4) is poured in plates of 9-10 cm, depth of agar is 3-4 mm.
METHOD OF STOKES DISC DIFFUSION
- Test culture is inoculated in middle portion of the plate and control cultures in upper and lower portions of the plate, leaving a zone of not more than 5 mm in between. Maximum 4 discs are put on a plate, two on either side.
INCUBATION
- The plate is incubated at 37°C for 18 hours.
INTERPRETATION OF STOKES DISC DIFFUSION
- Radii or zone of inhibition of test and control organisms are measured with a scale from the edge of the disc to edge of zone of inhibition.
- Sensitive – Zone equal to or larger or not more than 3 mm smaller than that of the control.
- Moderately sensitive – Zone radii more than 3 mm, and is also smaller than that of the control by more than 3 mm.
- Resistant – No zone or less than 3 mm radii.
ADVANTAGES OF STOKES DISC DIFFUSION
- Advantage of this method is that reading of the test strain is always taken in comparison to that of the control.
- So all the variables of Kirby-Bauer method like quality of agar, concentration of agar, strength of antibiotic discs are taken care of, as they affect both control and test strains equally.
- Blank discs can also be easily detected by this method.
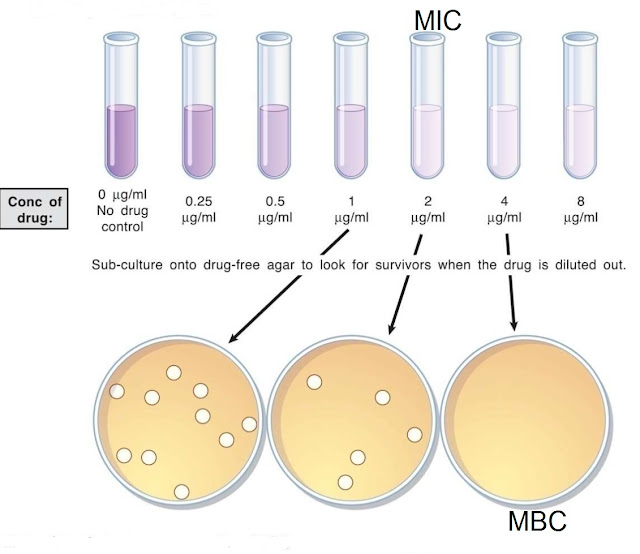
TUBE DILUTION METHOD
- Muller Hinton broth
METHOD
- Two sets of doubling dilutions of antibiotics are prepared in Muller Hinton broth, so that each tube contains 1 ml of diluted antibiotic.
- One set of tubes is inoculated with 0.5 ml of overnight broth culture of test organism diluted 1/100 and the other set of tubes with control organisms.
INCUBATION OF TUBE DILUTION METHOD
- They are incubated overnight at 37°C.
OBSERVATION OF TUBE DILUTION METHOD
- The last tube showing no growth is taken as the end point.
MIC
- Minimum inhibitory concentration is taken as the lowest concentration of the drug showing no growth.
MBC
- All tubes showing no growth are subcultured onto solid media.
- Minimum bactericidal concentration is taken as the lowest concentration of antibiotic yielding no growth on plate subculture and represents a kill of more than 99.99%.
PLATE DILUTION METHOD
METHOD
- This is done for MIC of organisms which grow poorly in broth.
- One ml of each strength of antibiotic is added to 19 ml of melted agar, cooled to 50°C.
- One loopful of overnight broth culture (diluted 1/100) is added to each concentration of antibiotic in agar.
- The lowest concentration of antibiotic completely inhibiting growth is the end point.
ADVANTAGE OF PLATE DILUTION METHOD
- Many strains may be tested on one plate.
FACTORS AFFECTING IN-VITRO ANTIBIOTIC SUSCEPTIBILITY TESTING
- Constituents of media
- pH of media
- Atmospheric conditions
- Thickness of medium
- Inoculum size
- Temperature
- Size of antibiotic molecules
- Concentration of discs.
ZONE SIZE INTERPRETATIVE CHARTS
- Zone size interpretative charts are charts depicting list of antibiotics along with their disc content (in mcg, IU etc.), diameters of zones of inhibition for Sensitive, Intermediate and Resistant findings.
- They are used as reference charts for interpretation of antibiotic sensitivity testing results.

No comments:
Post a Comment