Learning objectives:
1.
Kinetics of immune response in reference to various markers used for
laboratory diagnosis
2.
Pre-requisite for HIV testing
3.
NACO (National AIDS Control Organization) strategies for HIV diagnosis in
various conditions / situations
4. Specific tests
for HIV infection:
Screening tests (ERS) (antibody detection)
Rapid/ Simple test / ELISA
Supplemental tests (antibody detection)
Western blot assay
Confirmatory tests:
Detection of viral RNA / proviral DNA
5.
Tests to measure prognosis / monitoring progress of HIV infection
Kinetics of immune response –:
·
Viremia- Viral entry
into the body leads to a transient period of high-level viremia and p24
antigenemia.
·
Window period- 3 to 12 weeks. Virus remains in the blood but antibody does not appear
in the blood.
·
Later on Humoral response is evidenced by formation of antibodies against different antigens.
Following care should be taken (3Cs) while performing the test for
HIV.
·
Consent in written
format should be taken before the test is done.
·
Confidentiality of a positive test result is must.
·
Counselling (Pre-test and Post-test Counselling) should be provided to motivate the
individual and induce behavioral changes.
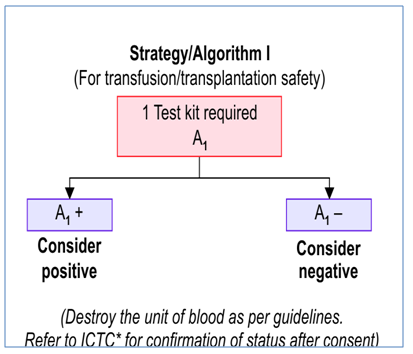
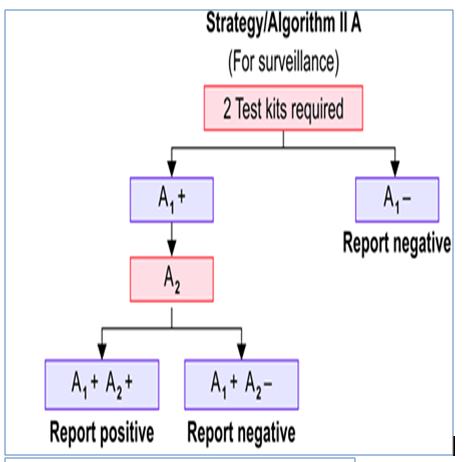
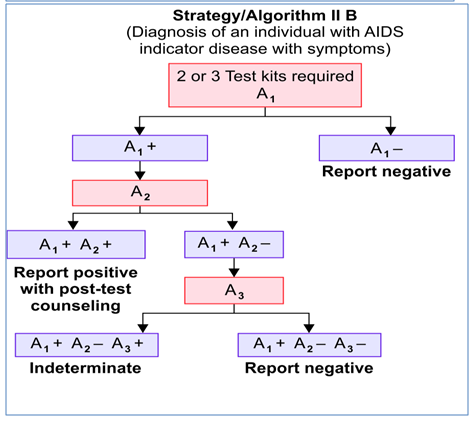
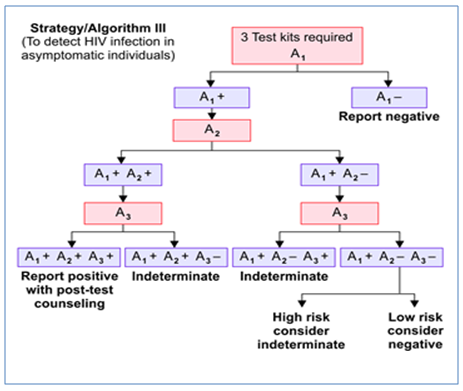
NACO STRATEGY FOR HIV DIAGNOSIS
NACO (National AIDS Control Organization, India) has formulated a strategic plan for HIV diagnosis.
Specific tests for HIV infection:
·
Screening tests (ERS) (antibodydetection)
o
Rapid/ Simple test / ELISA
·
Supplemental tests (antibody detection)
o Western blot assay
· Confirmatory tests
A) Screening tests (antibody detection tests):
·
Sample taken : blood in plain vaccute
1.
Rapid/ Simple test
Advantage:
·
Easy to perform and provide quick results (takes <
30 minutes).
·
Do not require special equipments.
Disadvantage:
· False positive results
· Results of a screening
test should never be used as the final .It is always subjected to confirmatory
tests
Most
commonly used rapid tests in India:
a.
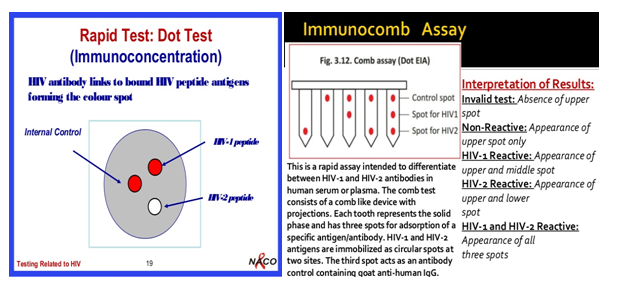
Dot blot assays
b.
Immunochromatography
c. Dip stick/ comb tests
1.
ELISA
Advantage:
·
Highly sensitive and specific
·
Adaptable to large number of samples and Cost effective.
Disadvantage:
·
Require special equipments like ELISA reader and
washer
·
Require
training of laboratory technician. Takes 2-4 hours.
A) Supplemental test or
confirmatory test:
1)
Western blot:
·
Principle: It detects individual antibodies in serum
separately against various antigenic fragments of HIV such as, Antibody to gag
gene products, pol gene productsand env gene products. The antigen antibody complexes appear as distinct
bands on nitrocellulose strip.
· Sample taken: Blood in plain vaccute
· WHO criteria i.e. presence of at least two envelope bands (out of gp120, gp160 or
gp41) with or without gag or pol bands
· CDC criteria-presence of any two out of p24, gp 120, gp160, gp41 bands
2)
Viral RNA detection
· The ‘gold standard’
method for confirmation of HIV diagnosis.
· Real time RT-PCR- for
estimating viral load
· Sample taken: blood in EDTA(plasma)
· Uses:
· For confirmation of
diagnosis of HIV/AIDS(can detects even few
copies of viral RNA)
· Diagnosis of HIV
during window period (earlier than all
available methods :12 days post exposure)
· Viral load monitoring-monitoring the response to antiretroviral therapy.
Early Infant
Diagnosis: Do not perform antibody estimation test . HIV DNA PCR is the test of
Choice.
Sample – Blood drawn from heel and taken on filter paper and dried - DBS (dried blood spots)/plasma



No comments:
Post a Comment