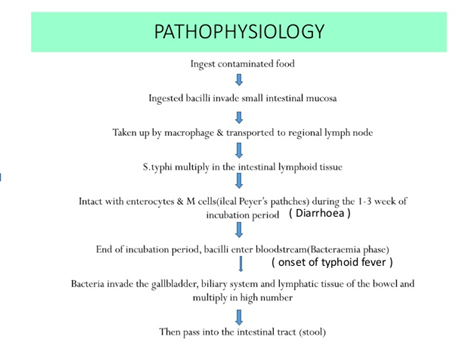
Enteric fever, also known as typhoid fever is an acute illness associated with fever caused by the Salmonella typhi bacteria. It can also be caused by Salmonella paratyphi, a related bacterium that usually causes a less severe illness (also known as paratyphoid fever)
The disease is transmitted by faecal-oral
route – via contaminated water and food.
LABORATORY
DIAGNOSIS
Specimen collection:
The best specimen for diagnosis is blood
for culture examination. The Serum sample is also very
useful for detection of antibodies during 2nd & 3rd
week of disease.
Following samples may be required for culture
examination in certain conditions
·
Urine (positive
in 2nd and 3rd week ,25% positivity)
·
Faeces (Valuable in patient on Antibiotic)
·
Bone-marrow (Recommended in
patient having high suspicious of enteric fever / PUO especially when blood
culture is negative)
·
Bile
Occasionally
the organisms can be isolated from Pus / CSF / Gall bladder / Mesenteric lymph
nodes
Laboratory
investigations:
There is no role of direct microscopic
examination from the specimen.
Following are the common investigations to be
carried out:
1.
Blood Culture – The gold
standard for diagnosis of typhoid fever
Volume of blood to be collected:
5-10 ml for Adult&1-3 ml for
children
The culture media used:
Hartley’s broth
- Check
for turbidity and evidence of growth after 1, 2, 3 and 7 days if bottles
showing signs of growth – Do culture on solid media in Mac Conkey agar and
Blood agar
On day 7, all the bottles sub-cultured
before being discarded as negative
- If
Automated system is used it gives indication for negative or positive.
If system indicates positive,
subculture from the bottle; & if system indicates negative, discard the
bottle and report it as negative.
2. Culture of other specimen:
Following culture media are used
- enrichment
media: Salanite F or tetrathionate broth
&
- Selective
media i.e DCA or Wilson - blair Media.
3.
Serological
test:
a.
Widal test
Widal test should be done after ONE WEEK of onset
of fever.
Principle:
It detects antibody & not bacteria or antigen.
b.
TyphiDot Rapid assay (detect
antibody)
c.
IgM dipstick test • Detects IgM
antibodies in serum and whole blood
d.
Enterocheck - WB •
Immunochromatographic test in cassette
4.
Other Non
specific Tests:
• Moderate
anemic, increased ESR, thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia
• Slightly
elevated PT and APTT, decreased fibrinogen level
• Liver
transaminases & bilirubin – increased 2 times than normal
• Mild
hyponatremia & hypokalemia
• Serum ALT: LDH > 9:1 = viral hepatitis
< 9:1 = typhoid hepatitis
5.
Molecular methods • PCR is
sensitive, but not widely used
DETECTION
OF CARRIERS
Detection of salmonella carriers can be done
in the following ways:
FEACAL carriers: can be detected by isolation
of bacilli from bile or feces. Repeated sampling increase chances of isolation.
Urinary carriers: can be detected by repeated
urine culture.
Detection of Vi agglutinin indicate recent
carrier.
1.
List the
investigations used for diagnosis of typhoid fever with reference to its
significance according to duration of diseases.
2. Draw labelled diagram of Tube widal test

No comments:
Post a Comment